Building a healthcare app is an exciting yet challenging endeavor, as the healthcare industry is one of the most impactful and highly regulated fields. With the rise in demand for digital healthcare solutions, apps are transforming how patients, providers, and administrators manage healthcare experiences, from remote patient monitoring to online consultations and appointment scheduling. If you’re thinking of developing a healthcare app, you’re taking on a project that not only has the potential to improve healthcare delivery but also to shape the future of digital health innovation.
Healthcare apps come in many forms and serve diverse purposes. Common categories include telemedicine apps, fitness and wellness apps, electronic health record (EHR) systems, mental health apps, medication tracking solutions, and health management apps designed for specific chronic conditions. Each of these has a unique set of features and compliance requirements, impacting both the development process and user experience. While every healthcare app has its nuances, building one follows a general pathway that involves careful planning, a strong understanding of healthcare needs, technical expertise, and adherence to strict regulations, especially those around data security and patient confidentiality.
For a healthcare app to succeed, it must provide a seamless user experience, prioritize patient privacy and data security, and meet regulatory compliance. Healthcare is a sensitive industry, and app developers must comply with rules like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe, or other region-specific regulations. Failure to meet these standards can lead to severe legal and financial consequences and diminish user trust. Beyond compliance, a successful healthcare app is one that patients and healthcare professionals find genuinely helpful, with intuitive design, accessible features, and accurate, real-time data.
A survey from Healthcare Dive emphasizes the growing role of AI in areas such as diagnostics, predictive analytics, and patient engagement. Innovations like AI-assisted image processing have reduced MRI and PET scan times by up to 60%, making diagnostics faster and more accessible. This aligns with the healthcare industry’s goals to improve service availability and enhance patient experiences in both clinical and retail environments, where wearable devices and telehealth are becoming increasingly common.
What is Healthcare App?
A healthcare app is a digital tool designed to assist patients, doctors, and healthcare providers in managing various aspects of health and medical care. These apps can serve a range of purposes, from helping individuals monitor their health and lifestyle to enabling healthcare professionals to streamline clinical workflows and enhance patient care.
Healthcare apps can include features such as telemedicine for virtual consultations, Electronic Health Records (EHR) access, appointment scheduling, medication tracking, and fitness or wellness tracking. They empower patients to take a proactive approach to their health, providing access to health data, reminders, and personalized health insights. For healthcare providers, these apps simplify patient management, improve communication, and support accurate diagnoses, making healthcare more accessible, efficient, and data-driven.
Healthcare apps come in various forms, serving different stakeholders within the healthcare ecosystem, including patients, doctors, hospitals, and insurance companies. They offer a range of functionalities, such as telemedicine solutions, electronic health records (EHR) access, appointment scheduling, medication management, and health tracking. By empowering users with easy access to health information and tools, Cenozic’s custom healthcare app development contributes significantly to proactive health management.
Benefits of Healthcare App
Healthcare apps bring significant benefits for both doctors and patients, enhancing the quality, accessibility, and efficiency of care. For doctors, healthcare apps simplify patient management and improve decision-making. With digital access to Electronic Health Records (EHRs), doctors can easily track patient histories, medication details, and treatment plans, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses. Telemedicine apps allow doctors to consult with patients remotely, expanding access to care and reducing the need for physical visits. Appointment scheduling and automated reminders help streamline administrative work, allowing doctors to focus more on patient care.
Real-time data sharing also improves collaboration with other healthcare providers, enhancing coordinated treatment plans and patient outcomes. With the increasing demand for efficient healthcare delivery, Cenozic’s expertise in healthcare software industry using AI and ML positions organizations to develop tailored apps that meet the unique needs of their patients and providers. By leveraging technology, healthcare apps can enhance accessibility, streamline operations, and ultimately lead to improved health outcomes for all stakeholders involved.
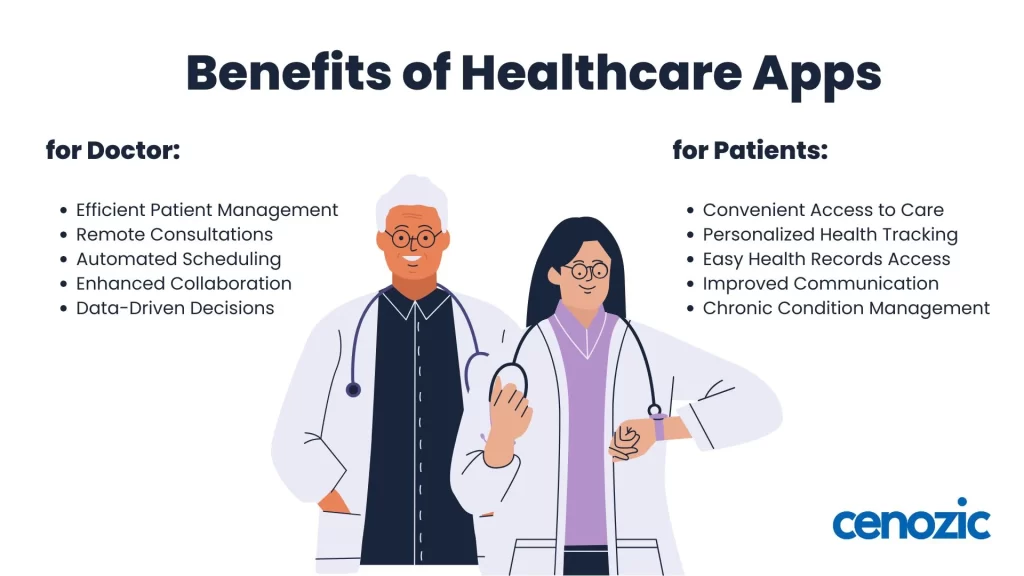
For patients, healthcare apps bring convenience and empowerment. Patients can schedule appointments, track medications, and consult with doctors from home through telemedicine, saving time and travel costs. Many apps allow patients to access their health data, such as lab results or medical history, fostering a proactive approach to their health management. Healthcare apps can offer reminders for medications and appointments, helping patients adhere to treatment plans and prevent complications.
Health tracking features, like step counters and calorie trackers, empower patients to adopt healthier lifestyles and manage chronic conditions effectively. By bridging communication gaps and making healthcare more accessible, healthcare apps benefit both doctors and patients, leading to more streamlined, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare.
Key Features of Healthcare Apps
Healthcare apps serve various purposes, catering to different stakeholders in the health ecosystem, including patients, doctors, healthcare facilities, and insurance companies. By leveraging technology, these applications can enhance patient engagement, streamline workflows, and improve overall healthcare outcomes. Healthcare apps often come equipped with a range of features tailored to meet the diverse needs of users. Common functionalities include:
- Telemedicine: Many healthcare apps provide telehealth services, allowing patients to consult with healthcare professionals remotely through video calls, chats, or voice calls. This feature is particularly valuable for patients in rural areas or those with mobility issues.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Some apps allow healthcare providers to access and update patient health records digitally. This access facilitates better decision-making and continuity of care.
- Appointment Scheduling: Users can book, reschedule, or cancel appointments easily through healthcare apps, reducing no-show rates and improving clinic efficiency.
- Medication Management: Healthcare apps can remind patients to take medications, track dosages, and provide refill alerts, ensuring adherence to treatment plans.
- Health Monitoring: Many apps offer features for tracking various health metrics, such as blood pressure, glucose levels, weight, and physical activity, empowering users to manage chronic conditions effectively.
Types of Healthcare App
Healthcare applications have gained significant traction in recent years, particularly with the rise of telemedicine and digital health solutions, revolutionizing how healthcare is delivered and experienced. Healthcare apps can be broadly categorized into several types, each serving specific functions:
- Patient-Centric Apps: These applications are primarily aimed at patients, helping them manage their health and wellness. They offer features like appointment scheduling, medication reminders, and health tracking. Popular examples include telehealth apps that allow users to consult with healthcare providers remotely, enabling better access to care. Apps like MyFitnessPal or Fitbit allow users to monitor their physical activity, nutrition, and overall wellness. Platforms such as Doctor on Demand and Zocdoc enable patients to connect with healthcare providers for virtual consultations.
- Provider-Centric Apps: Designed for healthcare professionals, these apps enhance clinical workflows and improve patient management. They often include Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems that allow providers to access and update patient records efficiently. These tools facilitate better communication among healthcare teams and support informed decision-making. Apps like Epic or Cerner that allow healthcare providers to access and manage patient records efficiently. Some apps like Clinical Decision Support Tools can provide healthcare professionals with evidence-based guidelines and alerts related to patient care.
- Health Management Apps: Focused on managing specific health conditions, these apps provide tailored support for patients with chronic diseases. They often include features for tracking symptoms, medications, and lifestyle changes. For instance, diabetes management apps help users monitor their glucose levels and dietary habits, promoting adherence to treatment plans. Apps designed for conditions like diabetes (e.g., Glucose Buddy) or hypertension (e.g., HeartHabit) help patients track their symptoms and medication adherence.
- Fitness and Wellness Apps: These applications encourage a healthy lifestyle by offering resources for fitness, nutrition, and mental well-being. They often include workout plans, dietary tracking, and mindfulness resources. Examples like MyFitnessPal help users log their meals and exercise routines to maintain a balanced lifestyle.
- Pharmacy Apps: Aimed at facilitating medication management, these apps provide services such as prescription refills, drug information, and reminders for taking medications. They enhance the patient experience by streamlining access to essential pharmacy services, often including home delivery options for added convenience. Apps like Medisafe help users remember to take their medications on time.
We’ll cover essential elements, including app types, the development process, must-have features, best practices for security, and how Cenozic can help you achieve your goal. Developing a healthcare app is a journey requiring patience, dedication, and a clear understanding of user needs, but with careful planning and a commitment to quality, you can make a significant impact in healthcare. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process, from ideation to deployment :
Step 1: Identify the Purpose and Target Audience
When starting a healthcare app, defining your purpose and target audience sets the foundation. First, outline the main goal—is it to improve patient care, streamline healthcare provider operations, or offer a wellness solution? The goal impacts the app’s functionality and features.

Dive into types of healthcare users: patients, providers, administrators, and public health entities. Research user pain points through surveys, industry reports, or interviews. For instance, patients often seek easy access to medical history and appointment scheduling, while providers may prioritize data accuracy and integration with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems.
In addition to healthcare roles, consider age demographics, tech literacy, and geographical locations. A telehealth app for seniors requires larger fonts and simpler navigation, while a fitness app for young adults might focus on customization and social features. Competitive analysis is crucial—identify similar apps, note their successes and gaps, and learn from them. Analyzing competitors helps refine your unique value proposition (UVP) by ensuring you meet unmet needs or improve on existing solutions.
Step 2: Research Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Healthcare is one of the most regulated sectors due to the sensitivity of health data. Begin with understanding HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the U.S., which ensures patient data privacy. Compliance involves encryption, access control, and audit trails, and breaches can incur severe penalties.
For European users, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) emphasizes data consent and right-to-access, making user permissions and data transparency mandatory. Compliance in each region may differ slightly; hence, apps that cater to multiple regions often have to adhere to layered regulatory frameworks. Designing a compliance checklist is beneficial. Include data storage and transfer encryption, user authentication, regular audits, and data anonymization techniques. Consulting legal experts or using compliance-centric development tools, like AWS’s HIPAA-eligible services, can streamline adherence.
Furthermore, many healthcare apps require medical device certifications (e.g., FDA clearance for the U.S.) if they offer diagnostic functionalities. Incorporating these elements into the early stages of app planning helps avoid costly redevelopment later.
Step 3: Select the Right Technology Stack
Your technology stack influences your app’s performance, scalability, and security. Key components include programming languages, frameworks, backend and frontend solutions, and data management tools. Choose languages and frameworks based on app needs. For instance:
- Native apps: Swift (iOS), Kotlin (Android)
- Cross-platform: React Native, Flutter, which allows code reuse and faster deployment.
Backend solutions vary: for real-time functionality, use Node.js or Django. For telemedicine apps with video calls, WebRTC enables live video and audio communication, and Firebase can manage real-time updates. Database choices depend on data types and volume. SQL databases (like PostgreSQL) ensure robust data handling for structured data, while NoSQL (MongoDB) can store flexible data like user preferences and notes.
Security solutions, such as SSL/TLS for encrypted data transfer, two-factor authentication, and regular software updates, are essential. Choosing HIPAA-compliant cloud services, such as AWS or Google Cloud, helps fulfill data protection standards.
Step 4: Design an Intuitive User Experience
User experience (UX) in healthcare apps goes beyond typical design—it requires accessibility, clarity, and compliance. Consider each user’s needs, including patients, doctors, and admin staff. A good starting point is user personas to understand behavior, challenges, and expectations.
Focus on a clean, easy-to-navigate interface that allows users to access services quickly. Features like large icons, legible fonts, and color contrasts benefit users with low tech literacy. Accessibility standards, including screen readers and touch-friendly buttons, should also be prioritized.
In healthcare, UX should minimize error risks—intuitive layouts for information input reduce data entry errors. Wireframes and prototyping let developers visualize workflows and improve based on user feedback. Regular usability tests, especially with real users, highlight areas for improvement before launch.
Privacy-centered design is critical; implement easy-to-understand consent forms and allow users to control their data. Feedback loops are invaluable post-launch, providing insights into UX optimization and feature refinement.
Step 5: Develop Key Features for Functionality and User Experience
Each healthcare app type has essential features. For example, telemedicine apps require video conferencing, appointment scheduling, and secure messaging. EHR apps focus on patient history, real-time updates, and data export capabilities.
For user engagement, notifications and reminders encourage consistent app usage, while in-app messaging enhances communication between patients and providers. Medication reminders or fitness tracking gamification are great examples of this.
Choose authentication options based on the app’s security needs. Biometric logins (face/fingerprint recognition) are ideal for security, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer. User feedback and rating systems build trust. When users feel their opinions matter, they’re more likely to stay engaged and recommend the app.
Step 6: Test, Launch, Gather Feedback, and Maintain the App
Rigorous testing ensures the app meets performance, security, and usability standards. Healthcare apps should undergo functionality testing, usability testing, compatibility testing, and security testing. Functionality testing ensures all features work as expected. For telehealth apps, this means verifying video/audio quality, messaging, and appointment scheduling. Security testing is critical in healthcare—penetration tests and vulnerability assessments identify potential data breaches.
Launch day is just the beginning. Collect feedback through in-app surveys or app store reviews to understand user satisfaction and areas for improvement. Regular updates based on feedback keep users engaged and ensure compliance with evolving regulations. Routine security checks and feature upgrades are essential for a healthcare app’s lifecycle.
Conclusion
Developing a healthcare app is a multifaceted endeavor that requires careful planning, execution, and adherence to industry regulations. From understanding the specific needs of your target audience to implementing robust security measures, each step is crucial in ensuring the success of your app. As the demand for digital health solutions continues to grow, healthcare apps are not just a trend; they are becoming essential tools for enhancing patient engagement, improving care delivery, and streamlining operations.
By focusing on user-centric design, integrating advanced technology, and ensuring compliance with healthcare standards, developers can create apps that truly make a difference in the healthcare landscape. Additionally, collaborating with experienced partners, like Cenozic, can provide the necessary expertise and resources to navigate the complexities of healthcare app development. Whether it’s through telehealth solutions, electronic health records integration, or custom patient management systems, the right approach can lead to innovative solutions that enhance the overall healthcare experience.
In conclusion, with the right strategy, tools, and expertise, your healthcare app can not only meet the needs of users but also transform how healthcare is delivered. As you embark on this journey, keep the focus on improving patient outcomes and leveraging technology to create a healthier future for all.

 iOS vs. Android: Which Platform Should You Choose for Your Mobile App?
iOS vs. Android: Which Platform Should You Choose for Your Mobile App?  The Future of AI: How Machine Learning is Transforming Businesses
The Future of AI: How Machine Learning is Transforming Businesses  AI in E-commerce: Enhancing Customer Experience & Engagement
AI in E-commerce: Enhancing Customer Experience & Engagement  How AI-Powered Chatbots Are Revolutionizing Customer Support
How AI-Powered Chatbots Are Revolutionizing Customer Support  The Role of AI in Mobile App Development: Smarter and Faster Apps
The Role of AI in Mobile App Development: Smarter and Faster Apps 


